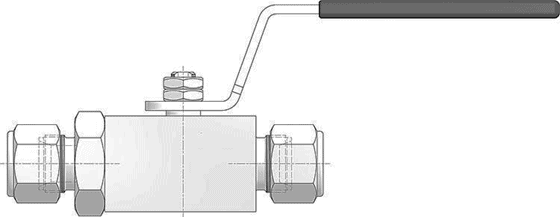
High Pressure Ball Valve
High Pressure Ball Valve
※ Size Range: 2″-24″
※ Class Range: 150LB-2500LB
※ Fire Safe Design
※ Anti Static
※ Anti blow-out
※ High Pressure Ball Valve Manufacturer
Introduction
A mechanical component that controls a fluid’s flow or pressure is commonly known as valve. High pressure ball valves are one of the several types of valves that are employed in different systems like industrial and marine hydraulics. The valves are referred to as high pressure valves when the flow line surpasses 150bar. The design of various valve components becomes crucial as the pressure rises.
Pressure, temperature ratings, as well as other parameters, are taken into consideration while high pressure ball valve manufacturers design its various components. Design calculations are performed for the valve housing, operating lever, connecting adapter, ball, and sealing cup. Different sealing cup materials are subjected to high pressure calculations to determine their maximum stresses and deflections. The breaking, running and terminating torques necessary to operate the valve is measured, and the results are matched with the technical details from the research case study.
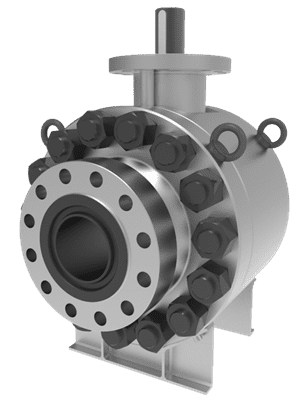
What is a High Pressure Ball Valve?
A high-pressure ball valve operates at high fluid pressure (between 500 and 700 bars), as the name indicates. The pressure that a valve can withstand decreases as its size increases and vice versa. These valves are employed in pipe systems with connections that have the same pressure load and are very robust. By rotating the lever 90 degrees, manual high-pressure ball valves can be opened and closed. Electric signals are used to replicate the functioning of motorized high-pressure ball valves. The valve is made of materials such as carbon steel and stainless steel 316. The stem, ball, and seat rings of valves must be made of a duplex or another material that is exceptionally durable. This increases the valve’s ability to handle high pressures and the actuator’s maximum permitted stem torque.
Working: High Pressure Ball valve.

The majority of ball valves, including high-pressure ball valves, operate similarly. The flow of liquids, gases, slurries, and abrasive fluids can be controlled by these quarter-turn valves. High-pressure ball valves may include swing checks integrated into the ball to function as check valves.
High-pressure ball valves are sometimes referred to as hydraulic ball valves since they are frequently employed in hydraulic systems across several sectors. You can control the flow of fluid moving through a pipeline at pressures of more than 3000 psi by using high-pressure hydraulic ball valves. An air actuated ball valve, for instance, might be installed in a hydroelectric power plant in order to regulate the flow of water running at a pressure as high as 7500 psi. The valve will be butt welded or screwed into the pipeline.
You must rotate the actuator 90 degrees in order to open the valve. When the actuator is turned, it moves the stem, which causes the ball to revolve. Just enough rotation will occur to align the hollow portion of the ball with the pipeline axis. The water will now flow freely through the valve to the opposite end of the pipeline. You need to rotate the actuator once more to completely make a 90-degree angle in order to terminate the flow. The ball will now be rotated such that the hollow side or bore is perpendicular to the pipe axis. The pressure from the onstream will force the ball and seats to tightly seal, stopping the flow.
Construction: High Pressure Ball Valve
- Body: The portion of a high-pressure ball valve that houses all of the valve’s internal parts is called the body. Strong metallic elements, like carbon steel and stainless steel, are used to make the body. To guarantee the longevity and effective operation of the valve, anti-static materials are also employed.
- Ball: Depending on the purpose of the valve, the ball is the part of a high-pressure ball valve constructed of sturdy material like steel. In a high-pressure ball valve, the ball controls whether fluid flow is blocked or permitted. The perforations on the ball surface improve consistent pressure distribution. Reduced bore or full-bore balls are both options for high-pressure ball valves. Reduced bore balls work well in applications where fluid flow pressure must be reduced by reducing flow. Where unhindered fluid flow is required, full-bore balls are employed.
- Stem:High-pressure ball valves consist of a stem that joins the operator or handwheel to the ball to improve fluid flow control. The stem is also composed of a sturdy material so that it can withstand high temperatures and pressures while transmitting the opening and closing torque. It should be made to be able to handle applications requiring cryogenic and high temperatures. Anti-blow-out stems are typically present in high-pressure ball valves so they can easily withstand the extra pressure.
- Seat: The seats, which are internal parts of a high-pressure ball valve, are strengthened with seat rings to guarantee a valve without leaks. The seat may be composed of metal or another material, such as an elastomer. To prevent damage from the continual pressure on the valve, elastomeric seat rings in high-pressure floating ball valves include O-ring seals.
- Actuators: Electric and manual controllers can be used to open and close high-pressure ball valves. The valve is often controlled by hand levers, pneumatic operators, and motor-driven actuators. In high-pressure operations or where trunnion mounted ball valves are employed, manual actuators are preferable. Electric actuators work well with floating ball valves or extremely high pressure applications.
Application: High Pressure Ball Valve
High-pressure ball valves are simple to use and offer stronger sealing. Furthermore, they can also handle corrosive media without suffering damage and are appropriate for essential tasks. For managing a variety of applications, high-pressure carbon steel ball valves are employed in a wide range of sectors.
High-pressure ball valves are employed in the petroleum and gas industries to control high-pressure activities across a wide range of temperatures. Ball valves are capable of managing a wide range of activities in an oil and gas industrial unit because they can withstand cryogenic and high-temperature operations.
Corrosion and abrasion resistance make stainless steel or carbon steel high-pressure ball valves ideal for controlling procedures involving delicate media. For instance, the pharmaceutical, food, and cosmetic industries regularly employ API-6D High-Pressure Ball Valves. To control the flow of delicate and corrosive fluids, all of these industries need high-pressure ball valves that are dependable, leak-proof, and robust.
In order to control high-pressure activities, 2-way and 3-way high-pressure ball valves are often employed in the hydraulic, cosmetic, pharmaceutical, and food industries. These ball valves are capable of controlling the direction of medium flow while maintaining tight shut-offs to prevent mixing or leakage of the various fluids or gases.
High pressure range ball valves are also appropriate for topside or subsea applications with a limited selection of possible structures and materials. For manual or automatically activated ball valves, duplex or strong materials with superior resilient qualities should be employed for the ball, seat rings, and stem in order to sustain pressure ratings and actuators’ maximum allowable stem torque (MAST), unless chosen by the client or when integrated with other operating conditions. Carbon steel, stainless steel, or other low alloys can also be employed in this situation.
Advantages: High Pressure Ball Valve
- High-pressure ball valves have been rigorously tested for strength which makes them suitable for high pressures.
- The thermal resistance of high-pressure ball valves is high allowing them to work in both lower and higher temperatures.
- Ball valves for high pressure are wear and corrosion proof making them suitable for a range of fluids.
- These valves are functional in fluids as well as in slurries.
- There are several pressure applications that are suited for high-pressure ball valves.
- The operation of these valves is simple.
- These valves are effective because they don’t require maintenance and offer a secure seal that is leak-free.
- Designs for high-pressure ball valves, such as the top entrance type, are simple to maintain and repair.
Differences: High Pressure & Low Pressure Ball Valves.
- Toilets and sinks, among other pieces of domestic hardware, have low-pressure ball valves. High-pressure ball valves are typically utilized in applications that require reliable shut-off power. In the oil and gas industry, they are often utilized for several applications.
- Low Pressure ball valves tend to be more common in industries where long-term reliability is important. They can resist pressures as high as 200 psi. Under some circumstances, a ball valve may also control the flow of high-pressure fluid. Whereas a high pressure ball valves, which have a small diameter in the ball and can withstand pressures of up to 500 pounds per square inch, are frequently used as backpressure and suction controls in pipelines, respectively. There is a considerable emphasis on design for high-pressure environments.
- Low-pressure ball valves are a great option for flow restriction since they have a high-pressure seal and a low-pressure construction. Gate valves are more effective and easier to use than ball valves, but they also cost more since they need more torque to work.
- High-Pressure Ball Valves are designed to control the flow of high-pressure fluids while maintaining fluid freedom of movement. They can be utilized, among other things, in pipe systems and flange connectors. They allow the system fluids to be safely separated when they are closed. If these fittings are not utilized in a flanged connection, water hammering may result.
Summary: High Pressure Ball Valve.
Choosing a valve for high-pressure processes requires taking into account a number of factors, including the valve’s material and leaking properties, even though high-pressure ball valves are frequently employed in chemical plants.
It’s important to understand the differences between low-pressure and high-pressure ball valves before making a decision. High-pressure ball valves are most frequently utilized in systems that need reliable power Backup. They are frequently employed in the oil and gas industries. Applications for these components include recirculation valves, suction controllers, and back-pressure valves.
You have a variety of alternatives to pick from if you’re looking to purchase ball valves. Even if you may find them through conventional searches, it is best to buy from a reputable specialist supplier because your specifications and dimensions are likely to be quite precise. Our valve specialists are accessible by email or phone if you have any more queries or need assistance choosing the appropriate valves for your project.